There are several methods for preparing alkyl polyglycosides or alkyl polyglucosides mixtures. Various synthetic methods range from stereotactic synthetic routes using protective groups (making compounds highly selective) to non-selective synthetic routes (mixing isomers with oligomers)。
Any manufacturing process suitable for use on an industrial scale must meet several criteria. It is most important to produce products with appropriate properties and economical processes. There are other aspects, such as minimizing side effects or waste and emissions. The technology used should be flexible so that the product’s performance and quality characteristics can be adapted to market requirements.
In the industrial production of alkyl polyglycosides, a process based on Fischer synthesis has been successful. Their development began about 20years ago and has accelerated over the past decade. Development during this period allowed the synthesis method to become more efficient and ultimately attractive for industrial applications. Optimizations work, particularly in the use of long-chain alcohols such as dodecanol/tetradecanol
(C12-14 -OH),have significantly improved product quality and process economy. The modern production plant base on Fischer Synthesis is the embodiment of low waste, zero emission technology. Another advantage of Fischer synthesis is that the average degree of polymerization of the products can be controlled over a wide range of precision. Therefore, related properties, such as hydrophilicity/water-solubility, can be adjusted to meet requirements. In addition, the raw material base is no longer affected by anhydrous glucose.
1. Raw materials for production of alkyl polyglycosides
1.1 Fatty Alcohols
Fatty alcohols can be obtained from petrochemical feedstocks(synthetic fatty alcohols) or from natural, renewable resources such as fats and oils (natural fatty alcohols). Fatty alcohol mixtures are used in the synthesis of alkyl glycosides to establish the hydrophobic part of the molecule. Natural fatty alcohols were obtained by transesteration and separation of fat and grease (triglyceride) to form corresponding fatty acid methyl ester, and hydrogenated. Depending on the length of the fatty alcohol alkyl chain required, the main ingredients are oils and fats: coconut or palm kernel oil for the C12-14 series, and tallow, palm or rapeseed oil for the C16-18 fatty alcohols.
1.2 Carbohydrate source
The hydrophilic portion of alkyl polyglycoside molecule is derived from a carbohydrate.
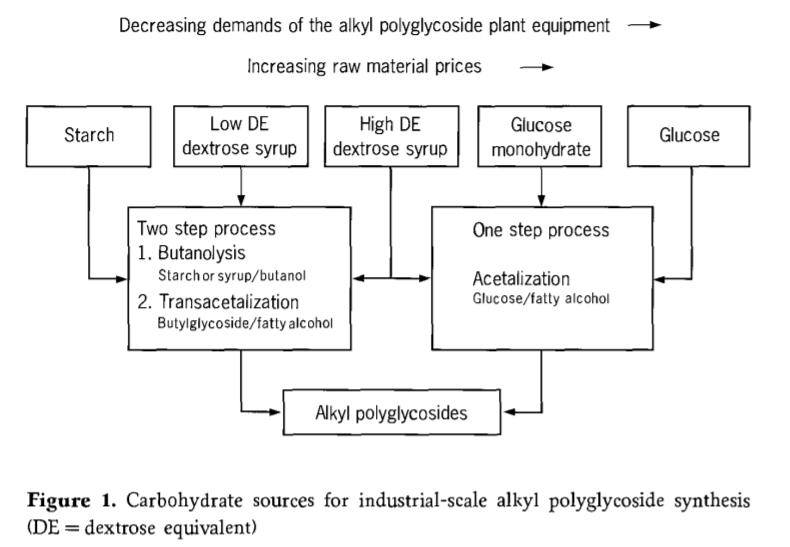
Macromolecular carbohydrates and monomer carbohydrates are based on starch of
corn, wheat or potato and can be used as raw materials for the preparation of alkyl glycosides. For example, polymer carbohydrates include low degradation levels of starch or glucose syrup, while monomer carbohydrates can be any form of glucose, such as anhydrous glucose, monohydrate glucose, or highly degraded glucose syrup.
Raw material choice influences not only raw material costs, but also production costs.
Generally speaking, raw material costs increase in the order starch/glucose syrup/glucose monohydrate/water-free glucose whereas plant equipment requirements and hence production costs decrease in the same order. (Figure 1)
Post time: Sep-28-2020





