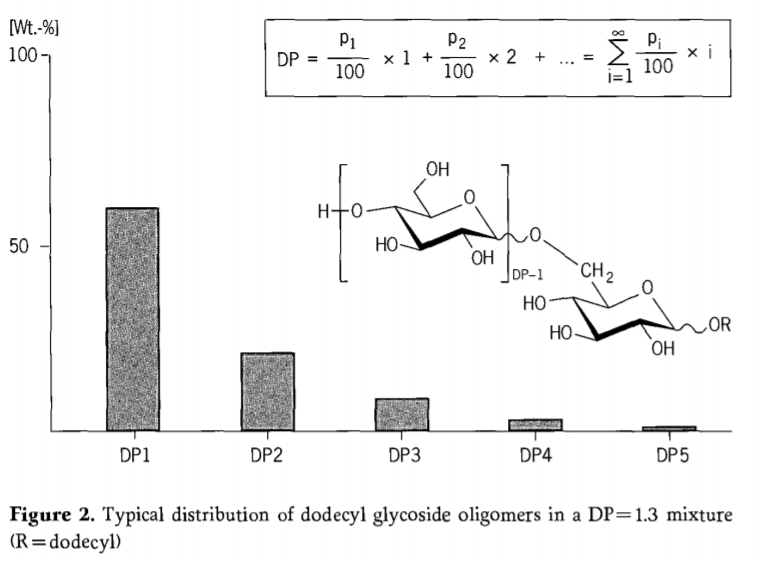
Through the polyfunctionality of carbohydrates, acid catalyzed Fischer reactions are conditioned to produce an oligomer mixture in which on average more than one glycation unit is attached to an alcohol microsphere. The average number of glycose units linked to an alcohol group is described as the (average) degree of polymerization (DPI. Figure2 shows the distribution for an alkyl polyglycoside with DP=1.3. In this mixture, the concentration of the individual oligomers (mono-,di-,tri-,-,glycoside) is largely dependent on the ratio of glucose to alcohol in the reaction mixture. The average degree of polymerization(DP) is an important characteristic with regard to the physical chemistry and applications of alkyl polyglycosides. In an equilibrium distribution, the DP- for a given alkyl chain length-correlates well with basic product properties, such as polarity, solubility, etc. In principle, this oligomer distribution can be described by P.J.Flory for describing the oligomer distribution of products based on polyfunctional monomers can also be applied to alkyl polyglucosides. This modified version of the Flory distribution describes alkyl polyglycosides as a mixture of statistically distributed oligomers.
The content of individual species in the oligomer mixture decreases with increasing degree of polymerization. The oligomer distribution obtained by this mathematical model accords well with analytical results (see Chapter 3). In simple terms, the average degree of polymerization(DP) of alkyl polyglycoside mixtures can be calculated from the mole percent pi of the respective oligomeric species “i” in the glycoside mixture (Figure 2)
Post time: Sep-28-2020





