Basically, the reaction process of all carbohydrates synthesized by Fischer with alkyl glycosides can be reduces to two process variants, namely, direct synthesis and transacetalization. In both cases, the reaction may proceed in batches or continuously.
Under direct synthesis, the carbohydrate reacts directly with the fatty alcohol to form the required long-chain alkyl polyglycoside. The carbohydrate used is often dried before the actual reaction( for example to remove the crystal-water in case of glucose monohydrate=dextrose). This drying step minimizes side reactions which take place in the presence of water.
In direct synthesis, the monomer solid glucose type is used as fine particulate solid.Since the reaction is an uneven solid/liquid reaction, the solid must be suspended completely in the alcohol.
Highly degraded glucose syrup (DE>96; DE=Dextrose equivalents) can react in a modified direct synthesis. the use of a second solvent and/or emulsifiers(for example alkyl polyglycoside) provides for a stable fine-droplet dispersion between alcohol and glucose syrup.
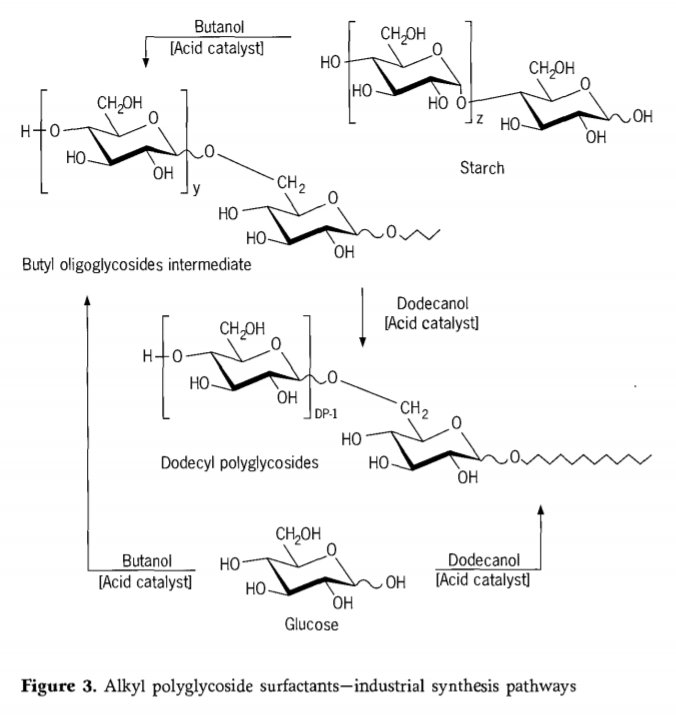
The two-stage transacetalization process requires more equipment than the direct synthesis. In the first stage, the carbohydrate reacts with a short-chain alcohol(for example n-butanol or propylene glycol) and optionally deploy-menzes. In the second stage, the short-chain alkyl glycoside is transacetalized with a relatively long-chain alcohol to form the required alkyl polyglycoside. If the molar ratio of carbohydrate to alcohol is the same, the oligomer distribution obtained in the process of transacetalization is basically the same as that obtained in the direct synthesis.
If oligo-and polyglycoses (for example starch,syrups with a low DE value)are used, the transacetalization process is applied. The necessary depolymerization of these starting materials requires temperatures of >140℃. It’s base on the alcohol used, this can create correspondingly higher pressures which impose more stringent demands on equipment and can lead to higher plant cost. In General, at the same capacity, the transacetalization process production cost higher than the direct synthesis. in addition to the two reaction stages, additional storage facilities must be provided, as well as optional work facilities for short-chain alcohols. Because of special impurities in starch (such as proteins), alkyl glycosides must undergo additional or finer refining. In a simplified transacetalization process, syrups with a high glucose content (DE>96%) or solid glucose types can react with short-chain alcohols under normal pressure, continues processes have been developed on this basis. (Figure 3 shows both synthesis routes for alkyl polyglycosides)
Post time: Sep-29-2020





