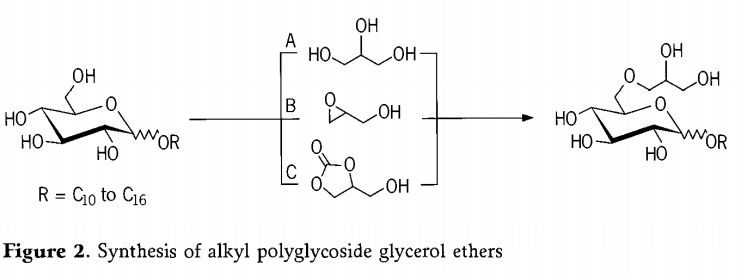
Synthesis of alkyl polyglycoside glycerol ethers
The synthesis of alkyl polyglycoside glycerol ethers was carried out by three different methods (Figure2, instead of the alkyl polyglycoside mixture, only the alkyl monoglycoside is shown as the educt). The etherification of alkyl polyglycoside with glycerol by method A proceeds under basic reaction conditions. The ring opening of an epoxide by method B likewise takes place in the presence of basic catalysts. An alternative is the reaction with glycerol carbonate by method C which is accompanied by the elimination of CO2 and which Presumably proceeds via an epoxide as intermediate stage.
The reaction mixture is then heated 200℃ over a period of 7 hours during which the water formed is continuously distilled off to displace the equilibrium as far as possible to the product side. As expected, alkyl polyglycoside di- and triglycerol ethers are formed in addition to the monoglycerol ether. Another secondary reaction is the self-condensation of glycerol to form oligoglycerols which are capable of reacting with the alkyl polyglycoside in the same way as the glycerol. Such high contents of higher oligomers can be entirely desirable because they further improve the hydrophilicity and hence for example the water solubility of the products. After the etherification, the products can be dissolved in water and bleached in a known manner, for example with hydrogen peroxide.
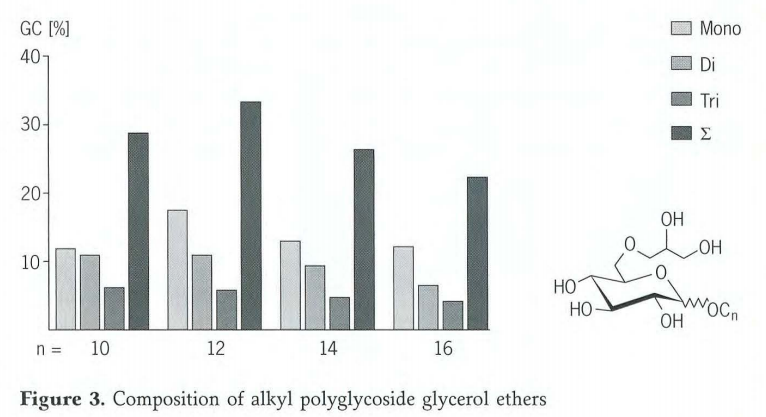
Under these reaction conditions, the degree of etherification of the products is independent of the alkyl chain length of the alkyl polyglycoside used. Figure3 shows the percentage contents of mono-,di- and triglycerol ethers in the crude product mixture for four different alkyl chain lengths. Reaction of the C12 alkyl polyglycoside provides a typical result. According to a gas chromatogram,mono-,di- and triglycerol ethers are formed in a ratio of approximately3:2:1. The total content of glycerol ethers is around 35%.
Post time: Mar-03-2021